1942 Obliquus Internus Abdominis Transversus Abdominis Original Vintage Print Anatomy
Internal abdominal oblique is a muscle found on the lateral side of the abdomen. It is broad and thin. it forms one of the layers of the lateral abdominal wall along with external oblique on the outer side and transverse abdominis on the inner side. Its fibers are obliquely oriented hence the name.
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/abdominal-internal-oblique-muscle/fEgn9BcTvy3juWnkrrJg_838_Bauchmuskeln_M._rectus_abdominis_M._obliquus_externus_abdominis_M._obliquus_internus_abdominis_FKT.png)
Musculus obliquus internus abdominis Anatomie Kenhub
Internal abdominal oblique muscle Musculus obliquus internus abdominis 1/5 Synonyms: none The aponeuroses of internal oblique, external oblique and transversus abdominis muscles extend vertically across the anterior aspect of the abdomen.
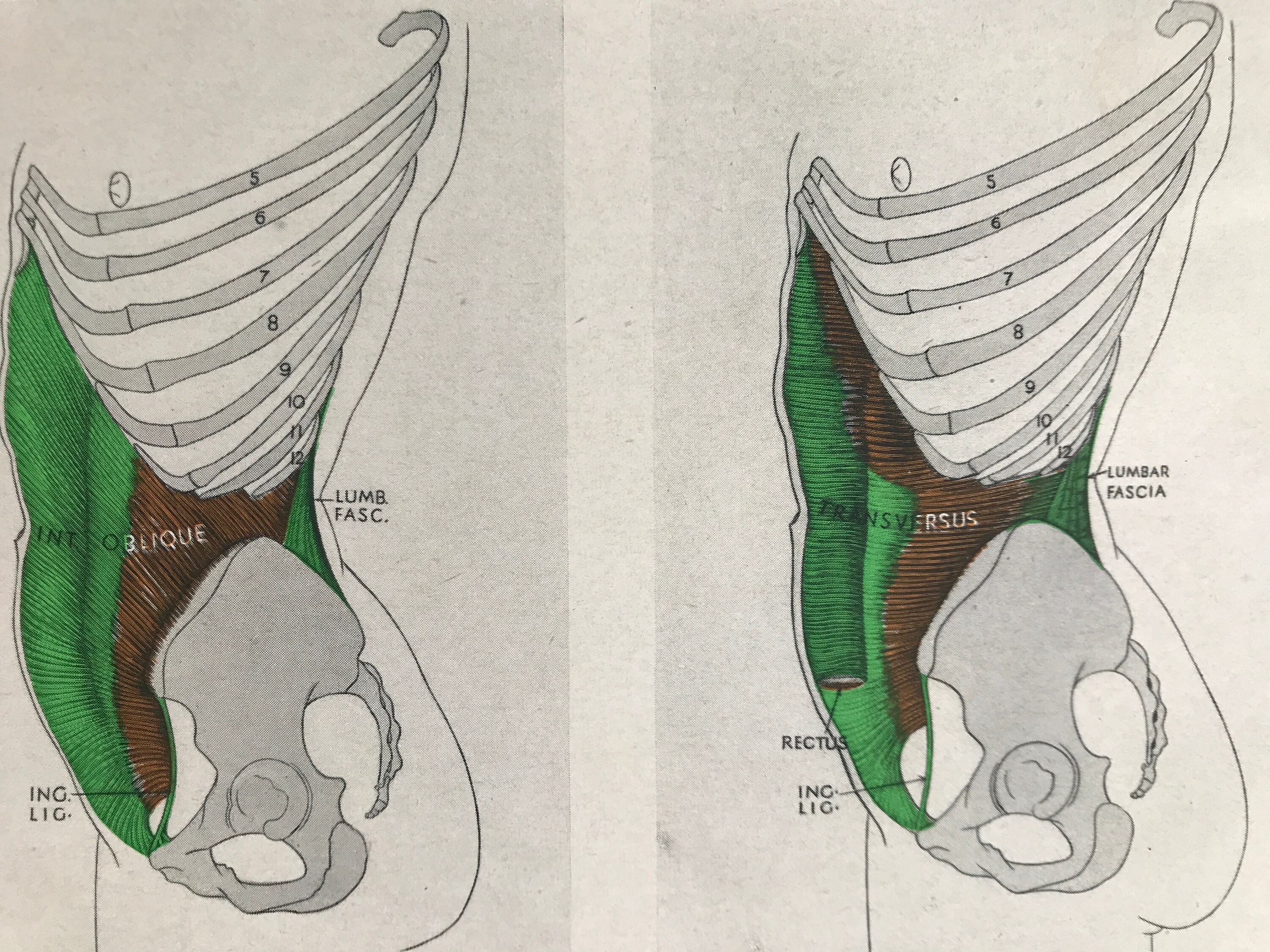
Základy sportovní kineziologie Fakulta sportovních studií
The internal oblique performs two major functions. Firstly as an accessory muscle of respiration, it acts as an antagonist (opponent) to the diaphragm, helping to reduce the volume of the chest cavity exhalation.
Conoce las funciones de los diferentes músculos abdominales
m. obliquus externus abdominis (external oblique muscle) m. obliquus internus abdominis (internal oblique muscle) Muscle Overview: Location, Shape, Function, Insertion, and Origin Location The oblique muscles are located on both sides of the abdomen (sides of waist). External obliques. Top layer, closest to the skin, running downwards and forwards.
CrossFit Lumbar Muscles, Part 2
Musculus obliquus internus abdominis. Definition. Origin: Tuber coxae. Insertion: Thirteenth rib and cartilage of the twelfth rib. Action: Compression and support of the abdominal viscera. Nerve: Medial branches of the last few.

Anatomy Stock Images torsoabdominalmusclesmusculusobliquesinternusinternaloblique
Transversus abdominis (TA), obliquus internus (OI), and obliquus externus (OE) are involved in multiple functions: breathing, control of trunk orientation, and stabilization of the pelvis and spine. How these functions are coordinated has received limited attention. We studied electromyographic (EMG) activity of right-sided muscles and 3.

M. obliquus internus YouTube
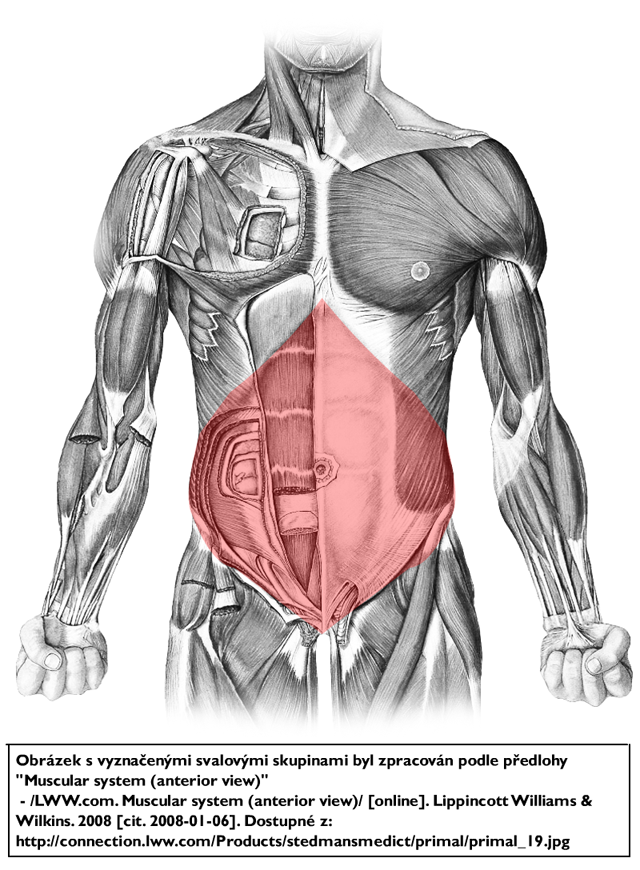
The anterolateral compartment contains five muscles, including the pyramidalis, the rectus abdominis, the tranversus abdominis, the external oblique, and the internal oblique.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-lateral-abdominal-muscles/0rYd1fO40tMQrdUB4j6lrw_Musculus_obliquus_internus_abdominis_02.png)
Internal oblique, external oblique, transversus muscle Kenhub
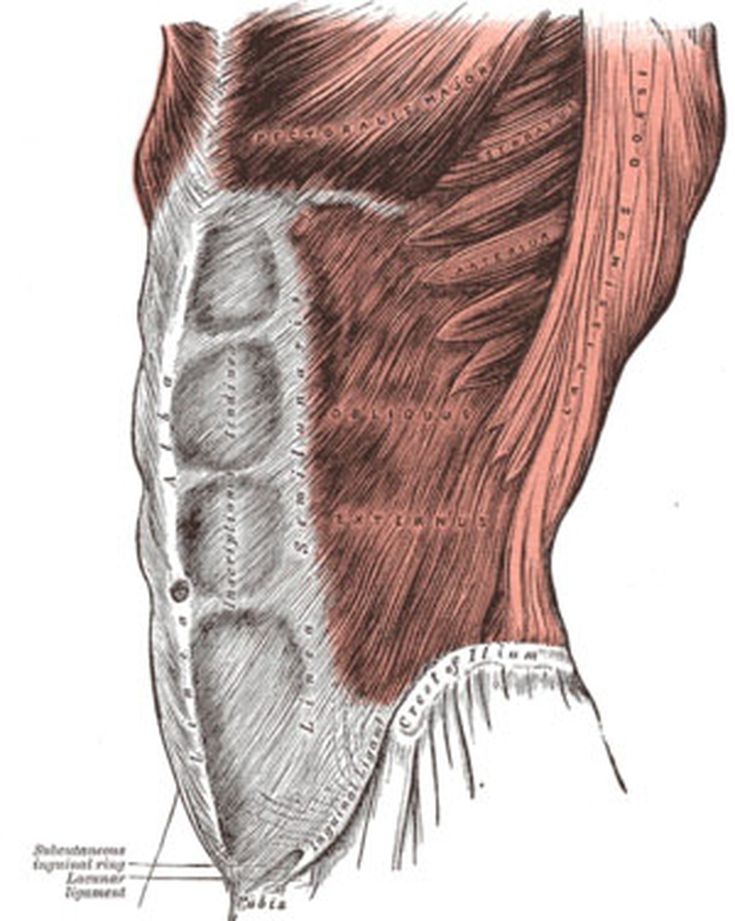
Description: The Obliquus internus abdominis (Internal or ascending oblique muscle), thinner and smaller than the Obliquus externus, beneath which it lies, is of an irregularly quadrilateral form, and situated at the lateral and anterior parts of the abdomen.

Základy sportovní kineziologie Fakulta sportovních studií
Both the obturator externus and obturator internus are bilateral-triangular shaped muscles. Generally, they originate from the obturator membrane and pelvic bone and attach to the greater trochanter of the femur. [1]
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1785/2bHNFfd8h6Zw5kyLrA6zLg_muscles-of-the-abdominal-wall_latin.jpg)
M. obliquus externus abdominis Anatomie und Funktion Kenhub
The posterior layer fuses with the aponeurosis of the transversus abdominis muscle and its upper portion inserts into the seventh, eighth, and ninth costal cartilages.. Successful Repair of M. obliquus Internus Abdominis Avulsion at the Iliac Crest—Operative Technique in Professional Soccer Players. April 11, 2023 | Orthopaedic Surgery.
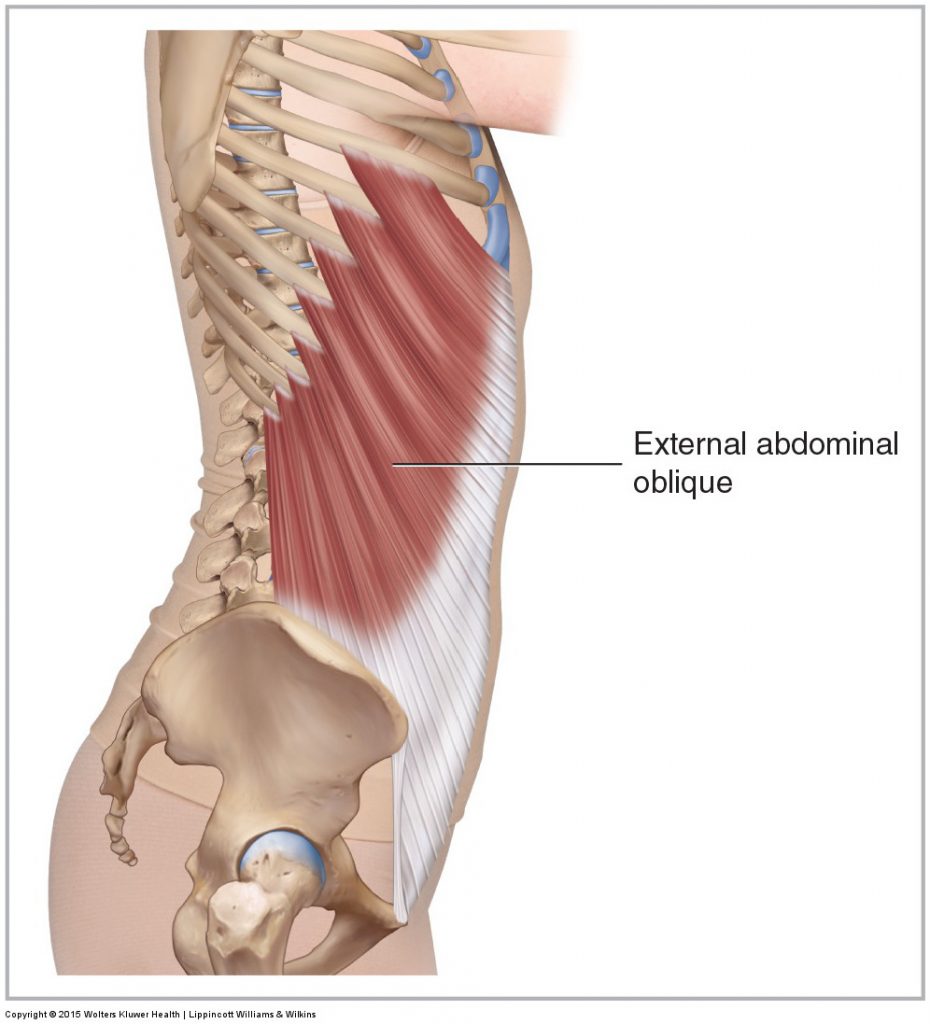
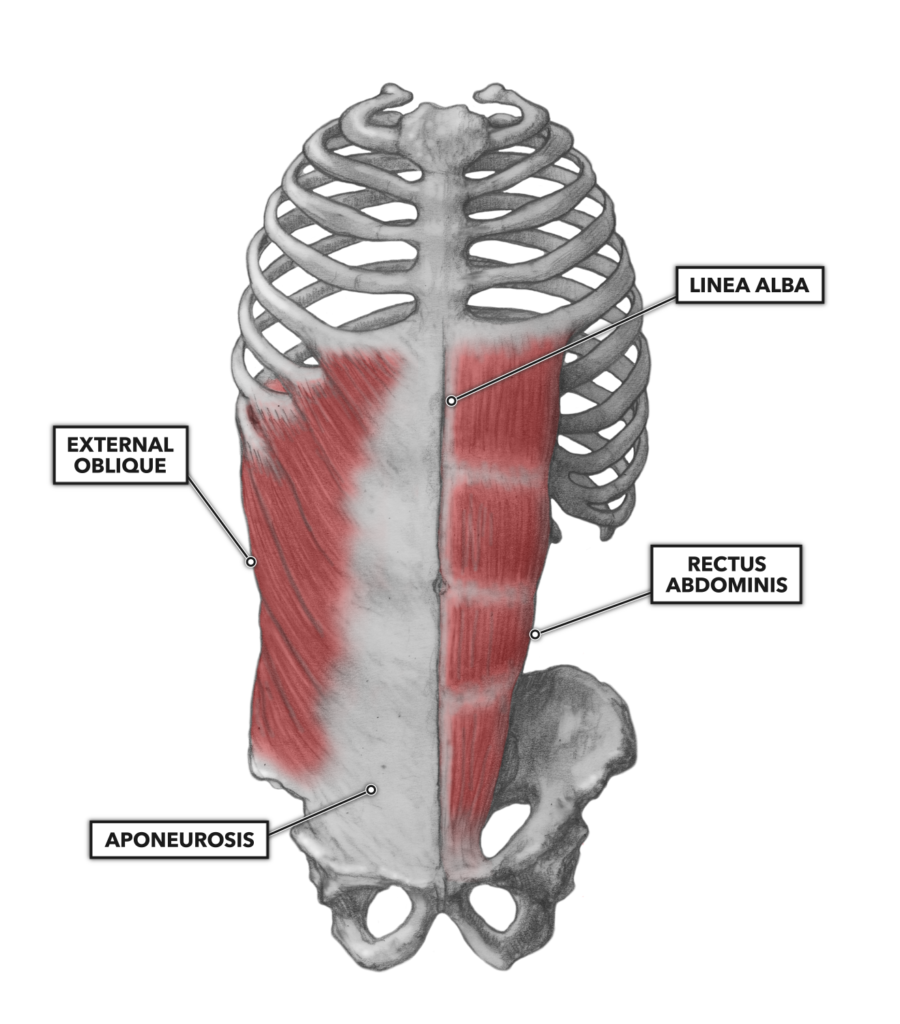
External Abdominal Oblique Learn Muscles
There were no associations between contraction thickness ratios in transversus abdominis or obliquus internus abdominis and pain at 1-year follow-up. Transversus abdominis lateral slide before intervention was marginally associated with a lower OR for clinically important improvement in pain at 1-year follow-up (OR 0.76, 95% CI 0.62 to 0.93)..
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/de/musculus-obliquus-internus-abdominis/MiOkVcAXHPYPQlsYVrxw_QMTXiV7Os42r3dphrxrCA_833_Thoraxmuskeln_ventral_NN.png)
Musculus obliquus internus abdominis Anatomie Kenhub
Introduction. Low back pain is relatively common among adolescent athletes, particularly baseball players 1,2).Lumbar stress fracture in the pars interarticularis (spondylolysis) is the most crucial differential diagnosis in this population 3).Such stress fractures usually start contralateral to the dominant arm, appearing as unilateral low back pain at onset 4,5).
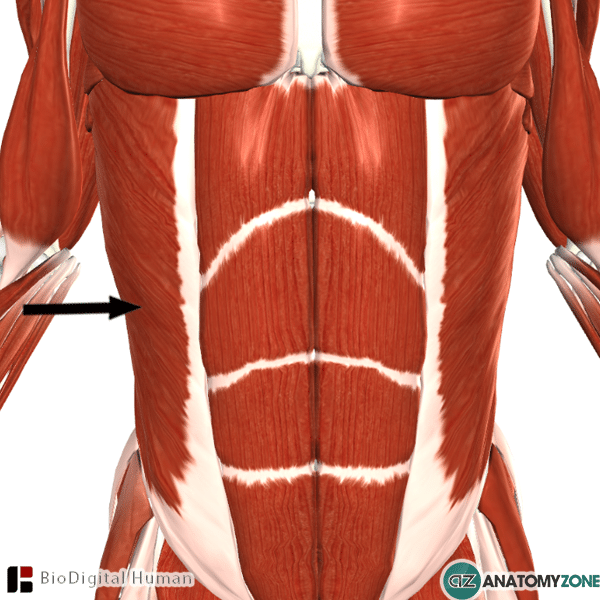
External Abdominal Oblique Muscle • Muscular, Musculoskeletal • AnatomyZone
To prevent confusions, be aware that in the textbooks it is uncommon to distinguish layers of the external oblique muscle, hence the internal abdominal oblique is most commonly described as the second, or middle layer of the lateral abdominal wall muscles. The complete video can be seen here.
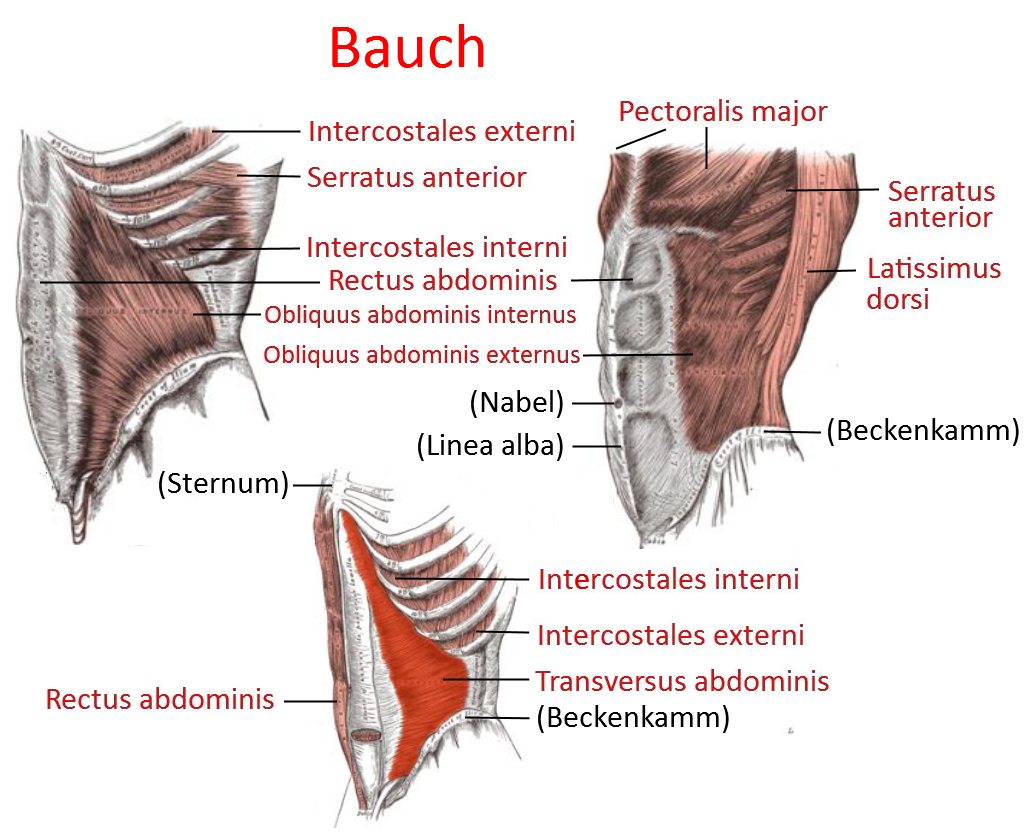
muskel obliquus internus abdominis Yogabuch
The internal oblique is an abdominal muscle located beneath the external abdominal oblique.
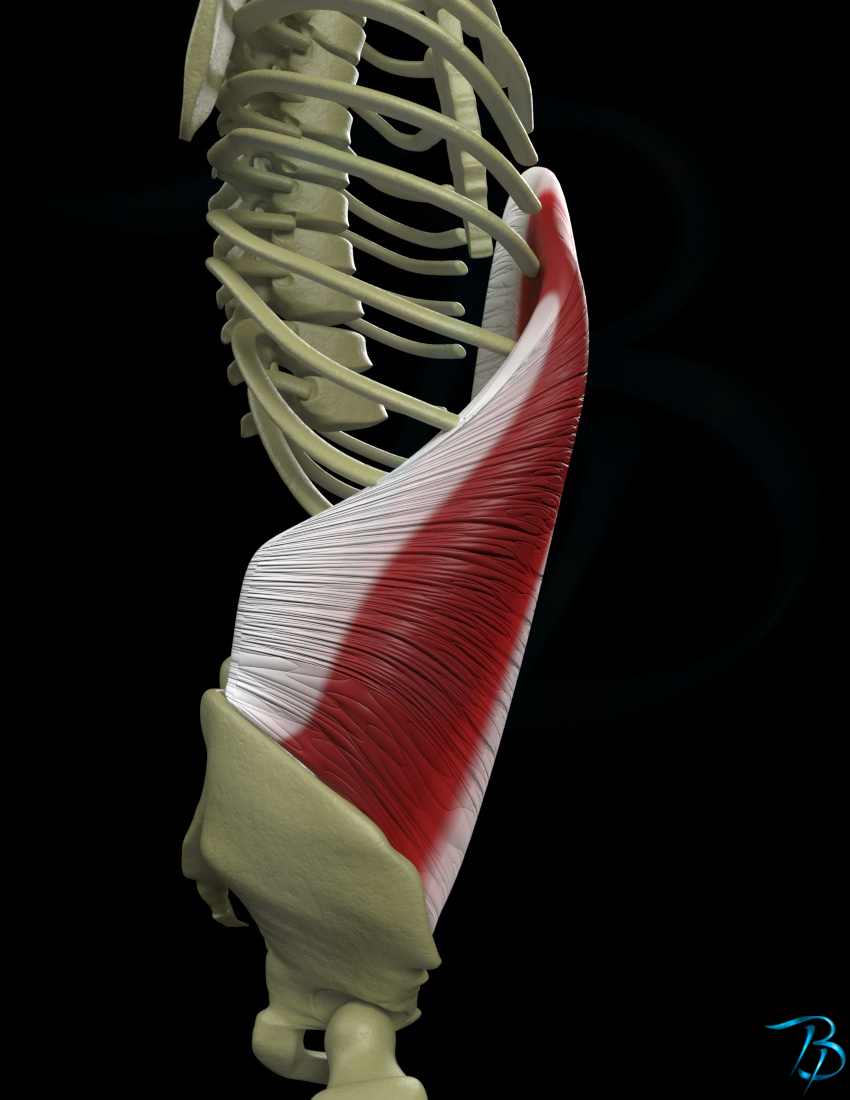
Obliquus internus abdominis Myoreflex
Overview. The internal oblique muscle (of the abdomen) is the intermediate muscle of the abdomen, lying just underneath the external oblique and just above (superficial to) the transverse abdominal muscle.. Structure. Its fibers run perpendicular to the external oblique muscle, beginning in the thoracolumbar fascia of the lower back, the anterior 2/3 of the iliac crest (upper part of hip bone.
What Is The Action Of Internal Oblique
The internal abdominal oblique is innervated by intercostal nerves 6-11 and the subcostal nerve. Functions Bilateral contraction of the internal oblique muscle aids in the flexion of the trunk and increasing intraabdominal pressure. Flexion of the trunk Unilateral contraction contributes to the lateral flexion and rotation of the trunk.